Objective-C 扩展了 C 语言,并加入了面向对象特性和 Smalltalk 式的消息传递机制。而这个扩展的核心是一个用 C 和 编译语言 写的 Runtime 库。它是 Objective-C 面向对象和动态机制的基石。
前言
当程序开始编译,到完全运行起来以后,为其提供相关支持的代码叫做“Objective-C运行期环境”(Objective-C runtime),它提供了一些使得对象之间能够传递消息的重要函数,并且包含创建示例所用的全部逻辑,Objc Runtime使得C具有了面向对象能力,在程序运行时创建,检查,修改类、对象和它们的方法,这里可以下到苹果维护的开源代码,苹果官方的Runtime编程指南
Runtime函数
Runtime系统是由一系列的函数和数据结构组成的公共接口动态共享库,在/usr/include/objc目录下可以看到头文件,可以用其中一些函数通过C语言实现objectivec中一样的功能。苹果官方文档里有详细的Runtime函数文档。
Class和Object基础数据结构
class
objc/runtime.h中objc_class结构体的定义如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
struct objc_class {
//isa指针指向Meta Class。后面会梳理对象 类 metaClass 的isa分别是什么。
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
// 父类
Class _Nullable super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 类名
const char * _Nonnull name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 类的版本信息,默认为0
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 类信息,供运行期使用的一些位标识
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 该类的实例变量大小
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 该类的成员变量结构体(暂未看到证明是其结构是链表的证明,留个坑)
struct objc_ivar_list * _Nullable ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
//方法定义的结构体(链表同上)
struct objc_method_list * _Nullable * _Nullable methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
//方法缓存,对象接到一个消息会根据isa指针查找消息对象,这时会在methodLists中遍历,如果cache了,常用的方法调用时就能够提高调用的效率。
struct objc_cache * _Nonnull cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
//协议链表(链表同上)
struct objc_protocol_list * _Nullable protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
/* Use `Class` instead of `struct objc_class *` */
objc_ivar_list和objc_method_list的定义
1 |
|
当类里面既有实例方法又有类方法时objc_method_list或出现两个此结构体,分别对象实例方法和类方法。
objc_cache
objc_class结构体中的cache字段用于缓存调用过的method。由于消息转发的机制所以需要缓存调用过的方法来提高执行效率1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
struct objc_cache {
//指定分配缓存bucket的总数。runtime使用这个字段确定线性查找数组的索引位置
unsigned int mask /* total = mask + 1 */ OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
//实际占用缓存bucket总数
unsigned int occupied OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
//指向Method数据结构指针的数组,这个数组的总数不能超过mask+1,但是指针是可能为空的,这就表示缓存bucket没有被占用,数组会随着时间增长。
Method buckets[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
};
objc_object与id
objc_object是一个类的实例结构体,objc/objc.h中objc_object是一个类的实例结构体定义如下:1
2
3
4
5
struct objc_object {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
typedef struct objc_object *id;
向object发送消息时,runtime库会根据object的isa指针找到这个实例object所属于的类,然后在类的方法列表以及父类方法列表寻找对应的方法运行。id是一个objc_object结构类型的指针,这个类型的对象能够转换成任何一种对象。
Meta Class
meta class是一个类对象的类,当向对象发消息,runtime会在这个对象所属类方法列表中查找发送消息对应的方法,但当向类发送消息时,runtime就会在这个类的meta class方法列表里查找。所有的meta class,包括Root class,Superclass,Subclass的isa都指向Root class的meta class,这样能够形成一个闭环。如图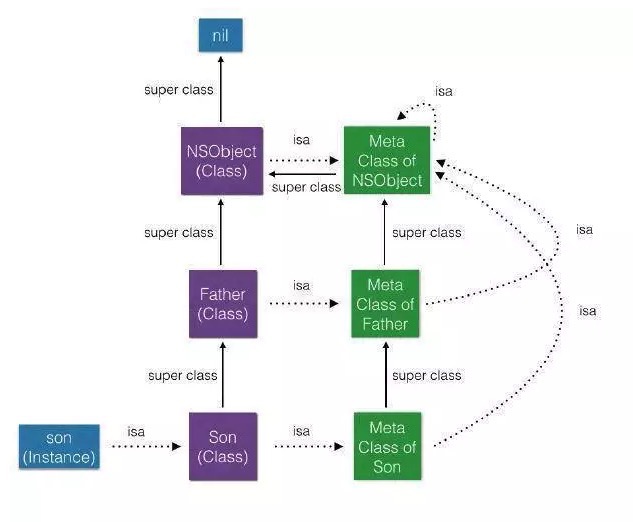
练习
1 |
|
运行结果
1 |
|
这里说明下几个方法注意的地方object_getClassName与class_getName1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// 获取类的类名 参数为class
class_getName(Class _Nullable cls)
// 返回给定对象的类名,返回的class会遵循上面的闭环关系(instance->类对象->metaClass->NSObject metaClass)
// 所以当传入的对象为metaClass时,metaClass对象的isa指向 NSObject 的metaClass,所以输出“NSObject”
object_getClassName(class)</code>
objc_getClass与object_getClass方法同样有上面的特性。
类与对象操作函数
runtime有很多的函数可以操作类和对象。类相关的一般是class为前缀,对象相关操作则一般是objc或object_为前缀。
类相关操作函数
className
1 |
|
super_class和meta-class
1 |
|
instance_size
1 | // 获取实例大小 |
成员变量(ivars)及属性
1 | //成员变量操作函数 |
methodLists
1 | // 添加方法 |
objc_protocol_list
1 | // 添加协议 |
version
1 |
|
练习
1 |
|
获取类定义
1 |
|
示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- (void)getClassDefine{
int numClasses;
Class * classes = NULL;
numClasses = objc_getClassList(NULL, 0);
if (numClasses > 0) {
classes = (Class *)malloc(sizeof(Class) * numClasses);
numClasses = objc_getClassList(classes, numClasses);
NSLog(@"number of classes: %d", numClasses);
for (int i = 0; i < numClasses; i++) {
Class cls = classes[i];
NSLog(@"class name: %s", class_getName(cls));
}
free(classes);
}
}
控制台输出结果1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
102019-05-23 17:52:30.639611+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: _CNZombie_
2019-05-23 17:52:30.639907+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: JSExport
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640085+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: NSLeafProxy
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640180+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: NSProxy
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640272+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: _UITargetedProxy
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640362+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: _UIViewServiceUIBehaviorProxy
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640478+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: _UIViewServiceReplyControlTrampoline
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640577+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: _UIViewServiceReplyAwaitingTrampoline
2019-05-23 17:52:30.640682+0800 runtimeDemo[55197:37325228] class name: _UIViewServiceImplicitAnimationDecodingProxy
--------------------------------------------等等还有更多------------------------------------------------------
实例操作函数
这些函数是针对创建的实例对象的一系列操作函数。
整个对象操作的函数
1 |
|
示例1
2
3
4
5
6
//把a转换成占用更多空间的子类b
NSObject *a = [[NSObject alloc] init];
id newB = object_copy(a, class_getInstanceSize(MyClass.class));
object_setClass(newB, MyClass.class);
object_dispose(a);
对象实例变量进行操作的函数
1 |
|
对对象类操作
1 |
|
动态创建类和对象
动态创建类
1 |
|
示例
1 |
|
最后输出为submethod1方法内容
动态创建对象
1 |
|
示例1
2
3
4
5
6//可以看出class_createInstance和alloc的不同
id theObject = class_createInstance(NSString.class, sizeof(unsigned));
id str1 = [theObject init];
NSLog(@"%@", [str1 class]);
id str2 = [[NSString alloc] initWithString:@"test"];
NSLog(@"%@", [str2 class]);
输出1
2
3//可以看到,使用class_createInstance函数获取的是NSString实例,而不是类簇中的默认占位符类__NSCFConstantString。
2014-10-23 12:46:50.781 RuntimeTest[4039:89088] NSString
2014-10-23 12:46:50.781 RuntimeTest[4039:89088] __NSCFConstantString
成员变量与属性
基础数据类型
Ivar
实例变量类型,指向objc_ivar结构体的指针,ivar指针地址是根据class结构体的地址加上基地址偏移字节得到的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16typedef struct objc_ivar *Ivar;
struct objc_ivar {
// 变量名
char *ivar_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 变量类型
char *ivar_type OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
// 基地址偏移字节
int ivar_offset OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#ifdef __LP64__
int space OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
}
objc_property_t
属性类型,指向objc_property结构体1
typedef struct objc_property *objc_property_t;
通过class_copyPropertyList和protocol_copyPropertyList方法获取类和协议的属性1
2objc_property_t *class_copyPropertyList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount)
objc_property_t *protocol_copyPropertyList(Protocol *proto, unsigned int *outCount)
示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
@interface PropertyTest : NSObject {
@public
NSNumber *anum;
NSString *bstring;
}
@property float alone;
@end
- (void)propertyList{
//获取属性列表
id PropertyTest = objc_getClass("PropertyTest");
unsigned int outCount;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(PropertyTest, &outCount);
for (int i = 0; i<outCount; i++) {
objc_property_t t = properties[i];
//查找属性名称
const char *cname = property_getName(t);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:cname];
//发掘属性名称和@encode类型字符串
const char *a = property_getAttributes(t);
NSString *attributes = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:a];
NSLog(@"propertyName = %@,attributes = %@",name,attributes);
}
}
- (void)ivarOffset{
PropertyTest *instance = [[PropertyTest alloc] init];
NSLog(@"PropertyTest address %p",instance);
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([PropertyTest class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char *name = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSLog(@"%s offset = %td",name,ivar_getOffset(ivar));
}
free(ivars);
NSLog(@"anum-----%p",&instance->anum);
NSLog(@"bstring-----%p",&instance->bstring);
}
输出1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//属性
2019-05-28 16:40:53.704703+0800 runtimeDemo[6030:1780788] propertyName = alone,attributes = Tf,V_alone
//ivar和对象地址的关系 对象地址为0x6000015c5160,加上偏移量8:0x6000015c5168(anum),加上16要进1:0x6000015c5170(bstring)
2019-05-28 17:29:59.126308+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] propertyName = alone,attributes = Tf,V_alone
2019-05-28 17:30:00.613843+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] PropertyTest address 0x6000015c5160
2019-05-28 17:30:19.015854+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] anum offset = 8
2019-05-28 17:30:28.354301+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] bstring offset = 16
2019-05-28 17:30:32.393656+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] _alone offset = 24
2019-05-28 17:30:32.393848+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] anum-----0x6000015c5168
2019-05-28 17:30:40.594590+0800 runtimeDemo[6530:1878614] bstring-----0x6000015c5170
关联对象
关联对象是在运行时添加的类似成员。
1 |
|
成员变量和属性的操作方法
成员变量
1 |
|
关联对象Associated Objects
1 |
|
属性
1 |
|
Method和消息
Method和消息的基础数据类型
SEL
选择器表示一个方法的selector的指针,可以理解为Method中的ID类型1
2
3
4
5
6
7
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
//objc_selector编译时会根据每个方法名字参数序列生成唯一标识
SEL sel1 = @selector(method1);
NSLog(@"sel : %p", sel1);
输出
2019-05-31 18:00:00.380537+0800 runtimeDemo[22289:3376242] sel : 0x1026a1a46
获取SEL的三个方法:1
2
3
4
sel_registerName(<#const char * _Nonnull str#>)
@selector(<#selector#>)
NSSelectorFromString(<#NSString * _Nonnull aSelectorName#>)
IMP
是函数指针,指向方法的首地址,通过SEL快速得到对应IMP,这时可以跳过Runtime消息传递机制直接执行函数,比直接向对象发消息高效。定义如下1
2
3
4
5
id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...)
//示例
((id(*)(id, SEL, NSInteger, NSInteger))imp2)(myClass, @selector(method3WithArg1:arg2:), 4, @"222");
imp();
Method
用于表示类定义中的方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method {
SEL method_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法名
char *method_types OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //是个char指针,存储着方法的参数类型和返回值类型
IMP method_imp OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法实现,函数指针
}
待续
Method相关操作函数
Method
1 |
|
Method的SEL
1 |
|
Method调用流程
消息函数,Objc中发送消息是用中括号把接收者和消息括起来,只到运行时才会把消息和方法实现绑定。1
2//这个函数将消息接收者和方法名作为基础参数。消息发送给一个对象时,objc_msgSend通过对象的isa指针获得类的结构体,先在Cache里找,找到就执行,没找到就在分发列表里查找方法的selector,没找到就通过objc_msgSend结构体中指向父类的指针找到父类,然后在父类分发列表找,直到root class(NSObject)。
objc_msgSend(receiver, selector, arg1, arg2, ...)
编译器会根据情况在objc_msgSend,objc_msgSend_stret,objc_msgSendSuper,或objc_msgSendSuper_stret四个方法中选一个调用。如果是传递给超类就会调用带super的函数,如果返回是数据结构而不是一个值就会调用带stret的函数。在i386平台返回类型为浮点消息会调用objc_msgSend_fpret函数。可参考我之前的一片文章关于self super。
Method中的接收消息对象参数和方法选择器参数
在Method中使用self关键字来引用实例本身,self的内容即接收消息的对象是在Method运行时被传入的同时还有方法选择器。
获取Method地址
使用NSObject提供的methodForSelector:方法可以获得Method的指针,通过指针调用实现代码。1
2
- (IMP)methodForSelector:(SEL)aSelector;
Method转发
如果使用[object message]调用方法,object无法响应message时就会报错。用performSelector…调用就要等到运行时才确定是否能接受,不能才崩溃。1
2
3
4
5
//先调用respondsToSelector:来判断一下
if ([self respondsToSelector:@selector(method)]) {
[self performSelector:@selector(method)];
}
Method转发机制分为三步:
动态方法解析
当对象收到无法响应的消息时,首先会调用如下方法:1
2
3
4//当消息类型为类方法时
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
//当消息类型为实例方法时
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
可以利用此方法实现预发crash 等功能。
备援接收者(重定向接收者)
1 |
|
当动态方法解析仍然无法处理时(返回值为NO),会继续调用下面的方法,同时在这里Runtime系统实际上是给了一个替换消息接收者的机会,但是替换的对象千万不要是self,那样会进入死循环。
示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
@interface FarwordingHelper : NSObject
@end
@implementation FarwordingHelper
- (void)method2{
NSLog(@"%@, %p", self, _cmd);
}
@end
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
//从定向消息接收者
[self test];
}
- (void)test {
[self performSelector:@selector(method2)];
}
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
NSLog(@"forwardingTargetForSelector");
NSString *selectorString = NSStringFromSelector(aSelector);
// 将消息转发给FarwordingHelper来处理
if ([selectorString isEqualToString:@"method2"]) {
return [[FarwordingHelper alloc] init];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
@end
最后进行转发
如果以上两种都没法处理未知消息就需要完整消息转发了。调用如下方法1
2
3
4
5
//这一步是最后机会将消息转发给其它对象,对象会将未处理的消息相关的selector,target和参数都封装在anInvocation中。forwardInvocation:像未知消息分发中心,将未知消息转发给其它对象。注意的是forwardInvocation:方法只有在消息接收对象无法正常响应消息时才被调用。
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
//必须重写这个方法,消息转发使用这个方法获得的信息创建NSInvocation对象。
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
NSMethodSignature *signature = [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
if (!signature) {
if ([FarwordingHelper instancesRespondToSelector:aSelector]) {
signature = [FarwordingHelper instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
}
return signature;
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
if ([FarwordingHelper instancesRespondToSelector:anInvocation.selector]) {
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[FarwordingHelper alloc] init]];
}
}
Protocol和Category
基础数据类型
Category
1 |
|
Category里面的方法加载过程,objc源码中找到objc-os.mm,函数_objc_init就是runtime的加载入口由libSystem调用,开始初始化,之后objc-runtime-new.mm里的map_images会加载map到内存,_read_images开始初始化这个map,这时会load所有Class,Protocol和Category,NSObject的+load方法就是这个时候调用的。下面是加载代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
// Discover categories.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
category_t **catlist = _getObjc2CategoryList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = catlist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
if (!cls) {
// Category's target class is missing (probably weak-linked).
// Disavow any knowledge of this category.
catlist[i] = nil;
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING category \?\?\?(%s) %p with ""missing weak-linked target class",cat->name, cat);
}
continue;
}
// Process this category.
// First, register the category with its target class.
// Then, rebuild the class's method lists (etc) if
// the class is realized.
BOOL classExists = NO;
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols || cat->instanceProperties){
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls, hi);
if (cls->isRealized()) {
remethodizeClass(cls);
classExists = YES;
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category -%s(%s) %s",
cls->nameForLogging(), cat->name,
classExists ? "on existing class" : "");
}
}
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols /* || cat->classProperties */){
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls->ISA(), hi);
if (cls->ISA()->isRealized()) {
remethodizeClass(cls->ISA());
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category +%s(%s)",
cls->nameForLogging(), cat->name);
}
}
}
}
//调用remethodizeClass方法,在其实现里调用attachCategoryMethods
static void
attachCategoryMethods(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flushCaches){
if (!cats) return;
if (PrintReplacedMethods) printReplacements(cls, cats);
bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
method_list_t **mlists = (method_list_t **)
_malloc_internal(cats->count * sizeof(*mlists));
// Count backwards through cats to get newest categories first
int mcount = 0;
int i = cats->count;
BOOL fromBundle = NO;
while (i--) {
method_list_t *mlist = cat_method_list(cats->list[i].cat, isMeta);
if (mlist) {
mlists[mcount++] = mlist;
fromBundle |= cats->list[i].fromBundle;
}
}
attachMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle, flushCaches);
_free_internal(mlists);
}
示例,下面的代码会编译错误,Runtime Crash还是会正常输出1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@interface NSObject (Sark)
+ (void)foo;
@end
@implementation NSObject (Sark)
- (void)foo{
NSLog(@"IMP: -[NSObject(Sark) foo]");
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
[NSObject foo];
[[NSObject new] foo];
}
return 0;
}
//结果,正常输出结果如下
2014-11-06 13:11:46.694 Test[14872:1110786] IMP: -[NSObject(Sark) foo]
2014-11-06 13:11:46.695 Test[14872:1110786] IMP: -[NSObject(Sark) foo]
objc runtime加载后NSObject的Sark Category被加载,头文件+(void)foo没有IMP,只会出现一个warning。被加到Class的Method list里的方法只有-(void)foo,Meta Class的方法列表里没有。
执行[NSObject foo]时,会在Meta Class的Method list里找,找不着就继续往super class里找,NSObject Meta Clas的super class是NSObject本身,这时在NSObject的Method list里就有foo这个方法了,能够正常输出。
执行[[NSObject new] foo]就简单的多了,[NSObject new]生成一个实例,实例的Method list是有foo方法的,于是正常输出。
Protocol
Protocol其实就是一个对象结构体1
2
3
4
5
6
7
#ifdef __OBJC__
@class Protocol;
#else
typedef struct objc_object Protocol;
#endif
操作函数
Category操作函数信息都包含在objc_class中,我们可以通过objc_class的操作函数来获取分类的操作函数信息。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
@interface RuntimeCategoryClass : NSObject
- (void)method1;
@end
@interface RuntimeCategoryClass (Category)
- (void)method2;
@end
@implementation RuntimeCategoryClass
- (void)method1 {
}
@end
@implementation RuntimeCategoryClass (Category)
- (void)method2 {
}
@end
- (void)testCategory {
NSLog(@"测试objc_class中的方法列表是否包含分类中的方法");
unsigned int outCount;
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList(RuntimeCategoryClass.class, &outCount);
for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i++) {
Method method = methodList[i];
const char *name = sel_getName(method_getName(method));
NSLog(@"RuntimeCategoryClass's method: %s", name);
if (strcmp(name, sel_getName(@selector(method2)))) {
NSLog(@"分类方法method2在objc_class的方法列表中");
}
}
}
//输出
2019-06-03 17:20:31.727172+0800 runtimeDemo[26975:3711641] 测试objc_class中的方法列表是否包含分类中的方法
2019-06-03 17:20:37.722456+0800 runtimeDemo[26975:3711641] RuntimeCategoryClass's method: method1
2019-06-03 17:20:37.722665+0800 runtimeDemo[26975:3711641] 分类方法method2在objc_class的方法列表中
2019-06-03 17:20:37.722788+0800 runtimeDemo[26975:3711641] RuntimeCategoryClass's method: method2
Runtime提供了Protocol的一系列函数操作,函数包括1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// 返回指定的协议
Protocol * objc_getProtocol ( const char *name );
// 获取运行时所知道的所有协议的数组
Protocol ** objc_copyProtocolList ( unsigned int *outCount );
// 创建新的协议实例
Protocol * objc_allocateProtocol ( const char *name );
// 在运行时中注册新创建的协议
void objc_registerProtocol ( Protocol *proto ); //创建一个新协议后必须使用这个进行注册这个新协议,但是注册后不能够再修改和添加新方法。
// 为协议添加方法
void protocol_addMethodDescription ( Protocol *proto, SEL name, const char *types, BOOL isRequiredMethod, BOOL isInstanceMethod );
// 添加一个已注册的协议到协议中
void protocol_addProtocol ( Protocol *proto, Protocol *addition );
// 为协议添加属性
void protocol_addProperty ( Protocol *proto, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount, BOOL isRequiredProperty, BOOL isInstanceProperty );
// 返回协议名
const char * protocol_getName ( Protocol *p );
// 测试两个协议是否相等
BOOL protocol_isEqual ( Protocol *proto, Protocol *other );
// 获取协议中指定条件的方法的方法描述数组
struct objc_method_description * protocol_copyMethodDescriptionList ( Protocol *p, BOOL isRequiredMethod, BOOL isInstanceMethod, unsigned int *outCount );
// 获取协议中指定方法的方法描述
struct objc_method_description protocol_getMethodDescription ( Protocol *p, SEL aSel, BOOL isRequiredMethod, BOOL isInstanceMethod );
// 获取协议中的属性列表
objc_property_t * protocol_copyPropertyList ( Protocol *proto, unsigned int *outCount );
// 获取协议的指定属性
objc_property_t protocol_getProperty ( Protocol *proto, const char *name, BOOL isRequiredProperty, BOOL isInstanceProperty );
// 获取协议采用的协议
Protocol ** protocol_copyProtocolList ( Protocol *proto, unsigned int *outCount );
// 查看协议是否采用了另一个协议
BOOL protocol_conformsToProtocol ( Protocol *proto, Protocol *other );
Runtime的应用
- Method Swizzling
利用Method Swizzling 和实现埋点,对老版本系统api兼容,黑盒调试等等。 - json Model
利用属性列表完成json->model 的转换