当我们按下 command+B之后发生了什么?App启动之前又做了什么?进程是如何创建的?主线程又是从哪里来的?ASLR如何生成的?
背景
本文的重点不在于“编译的细节(预处理,词法分析等等)”,而在于除了这些之外:xcode还做了什么。以及App启动之前,或者说dyld之前又做了什么。
下面开始第一部分:编译。
xcode build
xcode的构建主要是下面任务的集合:
- 源码的编译,链接。
- 资源(asset,storyBoard,headers)的拷贝和处理
代码签名校验和一些自定义的脚本。
同时这些任务是按照特定 的顺序来执行的:依赖关系。
我们可倒推一下这个依赖关系,如下(图片来源WWDC):

在构建的第一步就会解析项目的配置,构建依赖关系,这一步会形成一个“定向图”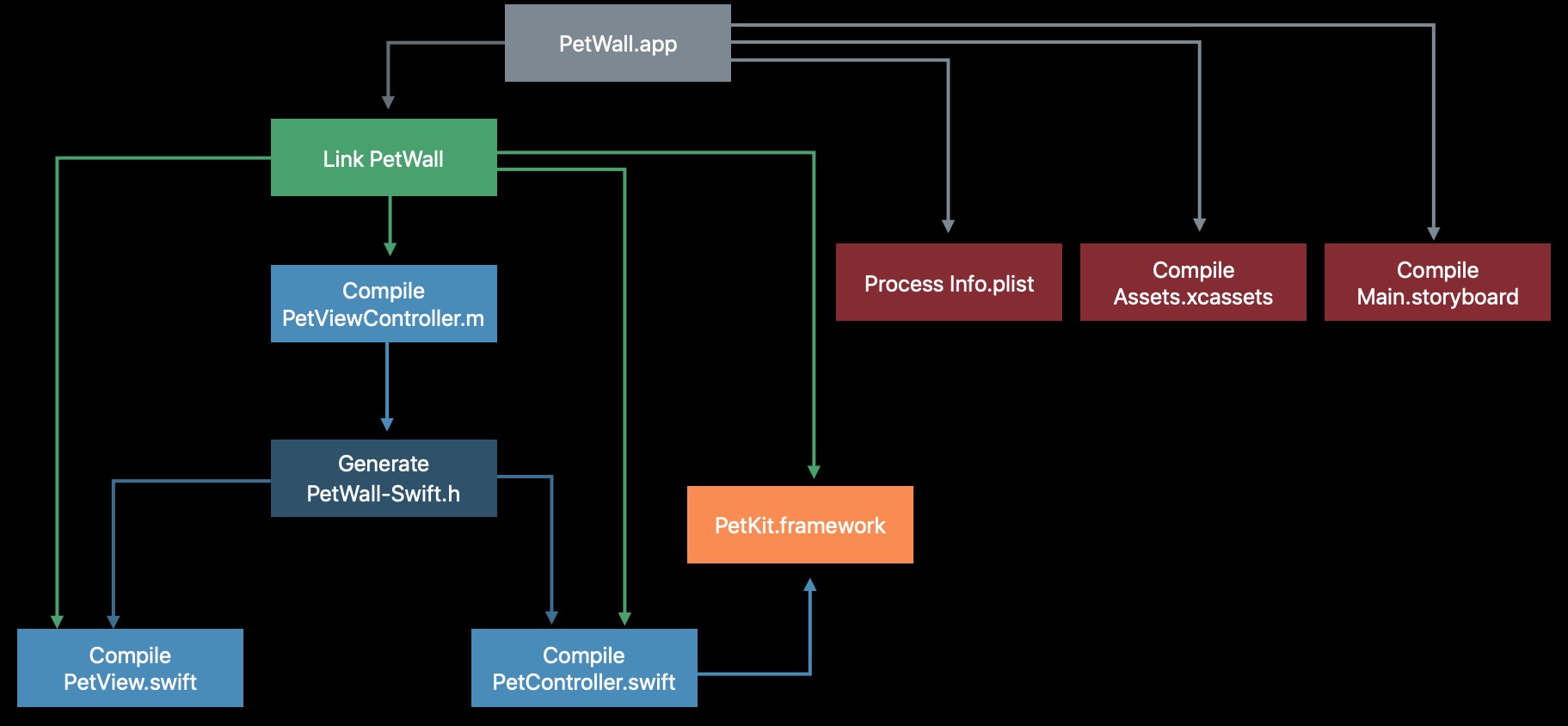
依赖的组成(来源)
依赖的来源主要有一下几个部分:
- xcode 内置的编译规则,比如:编译器,链接器,还有一些资源目录,这些规则决定了哪些是输入文件,哪些是输出。
- 显式声明的依赖关系:Target Dependencies
- 隐式声明的依赖关系:Linked Frameworks and Libraries
- Build Phase
构建优化
增量编译
通过上面的“定向图”,我们知道一次编辑,会执行上面的所有内容,为了提高编译速度,减少无效的任务,xcode使用了增量编译技术。
在每一个构建任务中,都会生成相应的签名,这个“签名”任务的输入路径、修改时间、编译器版本信息、有关任务的元数据等组成。
在构建之前会检查签名是否和当前一直,来决定是否跳过当前任务。
并行编译
在scheme的设置中,可以选择是否开启并行编译(默认开启)。
经测试,在有缓存的情况下如下:
开启并行:
关闭: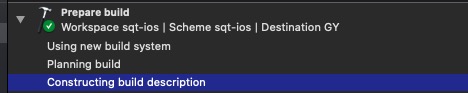

clean之后
开启并行:
关闭:
案例
这是作者的一个真实项目,我们先来看一下构建流程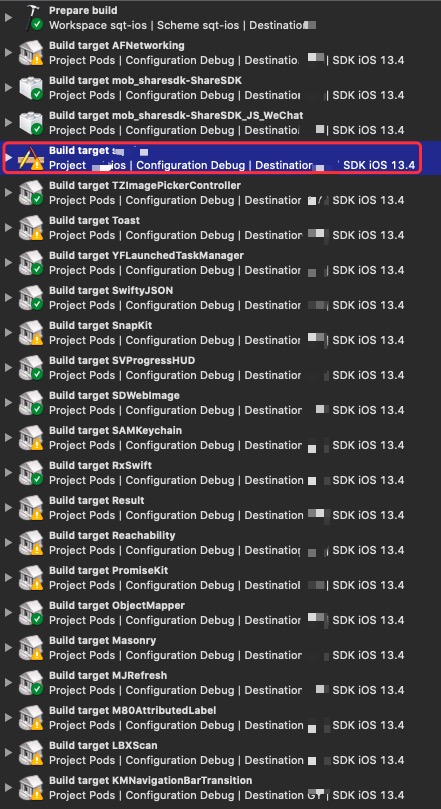
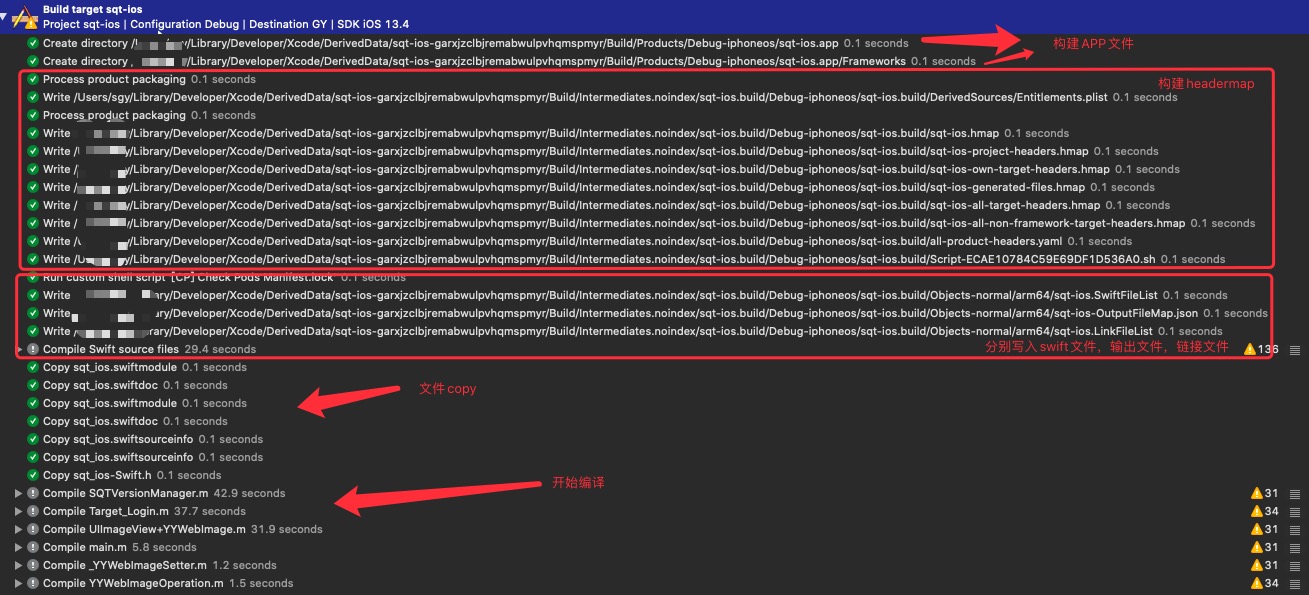
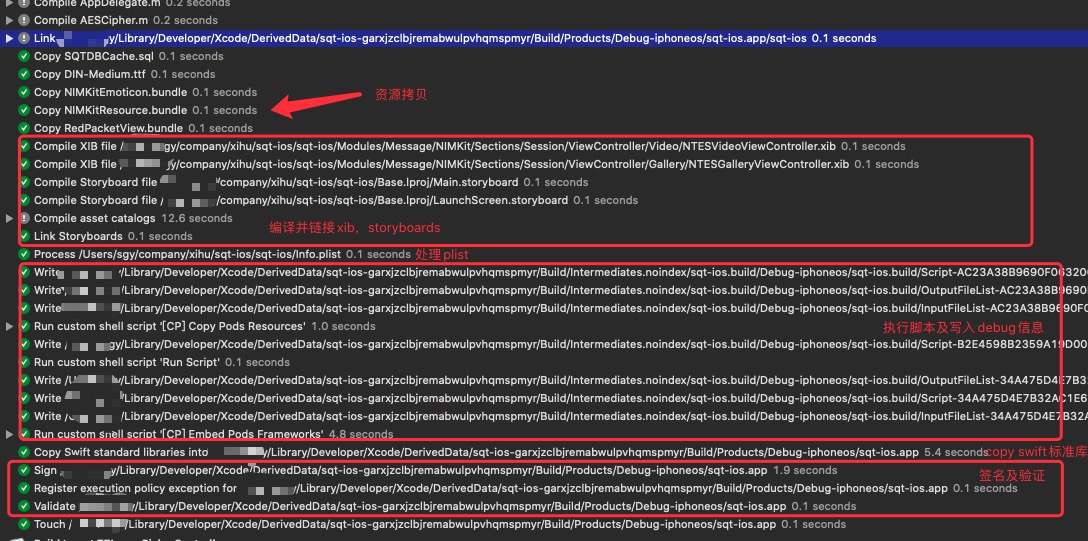
xcode 构建日志
先来大致梳理一下构建过程:
- 创建app包文件。
- 创建库目录。
- 文件写入。包括:Entitlements.plist,xxx.hmap。
- 执行CocoaPods的编译前脚本:检查Manifest.lock文件。
- 写入对应的,编译.m文件,生成.o文件。
- 编译assets,编译storyboard,链接storyboard。
- 写入debug信息。
- 执行CocoaPods编译后脚本:拷贝CocoaPods Target生成的Framework。
- 拷贝swift标准库。
- 签名并验证app。
下面我们来特别说明在wwdc中提到的,其中的一些步骤。
构建的第一个步骤是创建app文件。这个步骤只有在第一次构建的时候才会有创建,在后续的增量编译中,不会再重复创建。
headermap
先来看一下headermap内容。这里有个查看hmap的工具。
我们可以看到headermap其实就是编译器找到头文件的辅助文件:存储这头文件到其物理路径的映射关系。
再来看一下编译器是如何使用的。我们从构建日志中复制一个Compile的完整命令,再后面加上-v。
linkfilelist
这个文件包含了所有需要被链接的目标文件(.o),和Link Map File不同,前者是链接时就需要的辅助文件,后者是链接之后的产物。来看一个具体的文件1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/NIMSessionMessageContentView.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/SQTUserCommerceInfoModel.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/SQTAlipayAuthInfoAPI.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/SQTCommercaListVC.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/CTMediator+MemberList.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/SQTTopicSupportAPI.o
n/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/NIMVideoContentConfig.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/CALayer+YYAdd.o
/Users/xxx/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/sqt-ios-garxjzclbjremabwulpvhqmspmyr/Build/Intermediates.noindex/sqt-ios.build/Debug-iphoneos/sqt-ios.build/Objects-normal/arm64/SQTMemoryCache.o
下面来看一下什么时候被使用:
由于命令过长(demo为真实项目),这不在展开。
下面进入第二部分:App启动。
启动
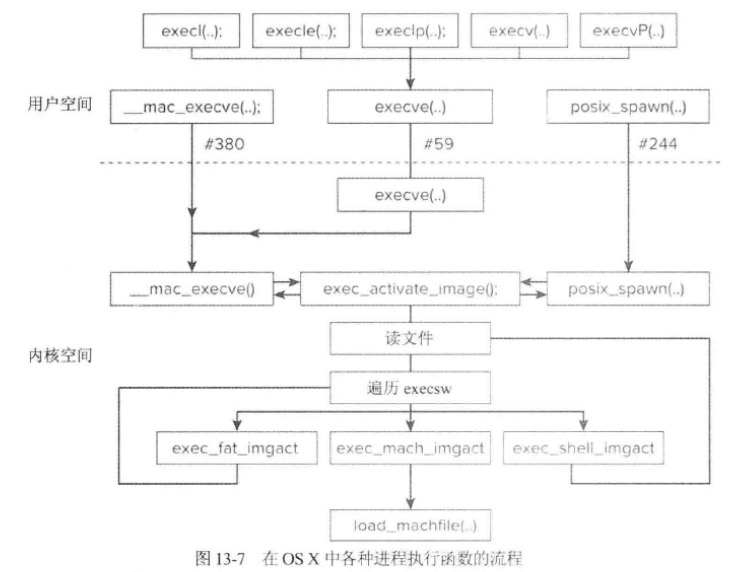
进程的创建
在UNIX模型中(也是OSX)模型,是不支持“空进程”或“新进程”的,同时进程不能被创建出来的,只能通过fork系统调用复制出来。如下图所示: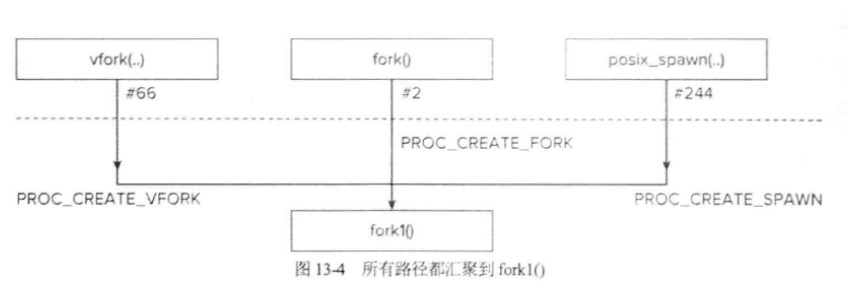
最终创建的流程会被汇总到fork1中,这里需要主要vfork流程并不会创建真正的mach层面的进程。而是由后面execve函数来进行真正的创建,这个在二进制加载章节会讲。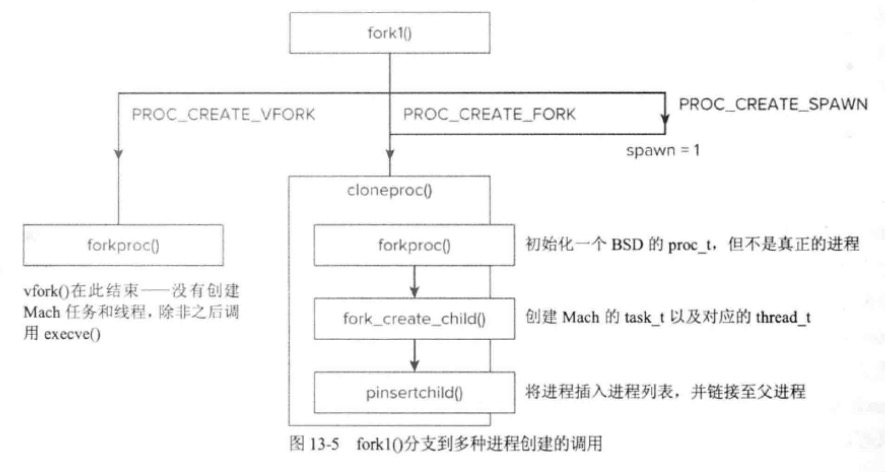
二进制文件的加载
经由上面流程“创建”出来的进程没有实质上的作用,除非执行了另外一个可执行程序。因此,进程创建的核心在于二进制文件的加载和执行。
__\mac_execve
进程创建的核心在于二进制文件的加载和执行,下面我们来查看一下加载过程1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
nt
__mac_execve(proc_t p, struct __mac_execve_args *uap, int32_t *retval)
{
char *bufp = NULL;
struct image_params *imgp;
struct vnode_attr *vap;
struct vnode_attr *origvap;
int error;
int is_64 = IS_64BIT_PROCESS(p);
struct vfs_context context;
struct uthread *uthread;
task_t old_task = current_task();
task_t new_task = NULL;
boolean_t should_release_proc_ref = FALSE;
boolean_t exec_done = FALSE;
boolean_t in_vfexec = FALSE;
void *inherit = NULL;
context.vc_thread = current_thread();
context.vc_ucred = kauth_cred_proc_ref(p); /* XXX must NOT be kauth_cred_get() */
/* Allocate a big chunk for locals instead of using stack since these
* structures a pretty big.
*/
//申请内存
MALLOC(bufp, char *, (sizeof(*imgp) + sizeof(*vap) + sizeof(*origvap)), M_TEMP, M_WAITOK | M_ZERO);
imgp = (struct image_params *) bufp;
if (bufp == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto exit_with_error;
}
vap = (struct vnode_attr *) (bufp + sizeof(*imgp));
origvap = (struct vnode_attr *) (bufp + sizeof(*imgp) + sizeof(*vap));
//初始化ip 结构
/* Initialize the common data in the image_params structure */
imgp->ip_user_fname = uap->fname;
imgp->ip_user_argv = uap->argp;
imgp->ip_user_envv = uap->envp;
imgp->ip_vattr = vap;
imgp->ip_origvattr = origvap;
imgp->ip_vfs_context = &context;
imgp->ip_flags = (is_64 ? IMGPF_WAS_64BIT_ADDR : IMGPF_NONE) | ((p->p_flag & P_DISABLE_ASLR) ? IMGPF_DISABLE_ASLR : IMGPF_NONE);
imgp->ip_seg = (is_64 ? UIO_USERSPACE64 : UIO_USERSPACE32);
imgp->ip_mac_return = 0;
imgp->ip_cs_error = OS_REASON_NULL;
imgp->ip_simulator_binary = IMGPF_SB_DEFAULT;
#if CONFIG_MACF
if (uap->mac_p != USER_ADDR_NULL) {
error = mac_execve_enter(uap->mac_p, imgp);
if (error) {
kauth_cred_unref(&context.vc_ucred);
goto exit_with_error;
}
}
#endif
//获取mach对应的bsd线程。thread_t->uthread_t
uthread = get_bsdthread_info(current_thread());
if (uthread->uu_flag & UT_VFORK) {
imgp->ip_flags |= IMGPF_VFORK_EXEC;
in_vfexec = TRUE;
} else {
imgp->ip_flags |= IMGPF_EXEC;
/*
* For execve case, create a new task and thread
* which points to current_proc. The current_proc will point
* to the new task after image activation and proc ref drain.
*
* proc (current_proc) <----- old_task (current_task)
* ^ | ^
* | | |
* | ----------------------------------
* |
* --------- new_task (task marked as TF_EXEC_COPY)
*
* After image activation, the proc will point to the new task
* and would look like following.
*
* proc (current_proc) <----- old_task (current_task, marked as TPF_DID_EXEC)
* ^ |
* | |
* | ----------> new_task
* | |
* -----------------
*
* During exec any transition from new_task -> proc is fine, but don't allow
* transition from proc->task, since it will modify old_task.
*/
imgp->ip_new_thread = fork_create_child(old_task,
NULL,
p,
FALSE,
p->p_flag & P_LP64,
task_get_64bit_data(old_task),
TRUE);
/* task and thread ref returned by fork_create_child */
if (imgp->ip_new_thread == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto exit_with_error;
}
new_task = get_threadtask(imgp->ip_new_thread);
context.vc_thread = imgp->ip_new_thread;
}
//处理二进制的主要逻辑
error = exec_activate_image(imgp);
/* thread and task ref returned for vfexec case */
if (imgp->ip_new_thread != NULL) {
/*
* task reference might be returned by exec_activate_image
* for vfexec.
*/
new_task = get_threadtask(imgp->ip_new_thread);
#if defined(HAS_APPLE_PAC)
ml_task_set_disable_user_jop(new_task, imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_NOJOP ? TRUE : FALSE);
ml_thread_set_disable_user_jop(imgp->ip_new_thread, imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_NOJOP ? TRUE : FALSE);
#endif
}
if (!error && !in_vfexec) {
p = proc_exec_switch_task(p, old_task, new_task, imgp->ip_new_thread);
/* proc ref returned */
should_release_proc_ref = TRUE;
/*
* Need to transfer pending watch port boosts to the new task while still making
* sure that the old task remains in the importance linkage. Create an importance
* linkage from old task to new task, then switch the task importance base
* of old task and new task. After the switch the port watch boost will be
* boosting the new task and new task will be donating importance to old task.
*/
inherit = ipc_importance_exec_switch_task(old_task, new_task);
}
kauth_cred_unref(&context.vc_ucred);
/* Image not claimed by any activator? */
if (error == -1) {
error = ENOEXEC;
}
if (!error) {
exec_done = TRUE;
assert(imgp->ip_new_thread != NULL);
exec_resettextvp(p, imgp);
error = check_for_signature(p, imgp);
}
/* flag exec has occurred, notify only if it has not failed due to FP Key error */
if (exec_done && ((p->p_lflag & P_LTERM_DECRYPTFAIL) == 0)) {
proc_knote(p, NOTE_EXEC);
}
if (imgp->ip_vp != NULLVP) {
vnode_put(imgp->ip_vp);
}
if (imgp->ip_scriptvp != NULLVP) {
vnode_put(imgp->ip_scriptvp);
}
if (imgp->ip_strings) {
execargs_free(imgp);
}
#if CONFIG_MACF
if (imgp->ip_execlabelp) {
mac_cred_label_free(imgp->ip_execlabelp);
}
if (imgp->ip_scriptlabelp) {
mac_vnode_label_free(imgp->ip_scriptlabelp);
}
#endif
if (imgp->ip_cs_error != OS_REASON_NULL) {
os_reason_free(imgp->ip_cs_error);
imgp->ip_cs_error = OS_REASON_NULL;
}
if (!error) {
/*
* We need to initialize the bank context behind the protection of
* the proc_trans lock to prevent a race with exit. We can't do this during
* exec_activate_image because task_bank_init checks entitlements that
* aren't loaded until subsequent calls (including exec_resettextvp).
*/
error = proc_transstart(p, 0, 0);
}
if (!error) {
task_bank_init(new_task);
proc_transend(p, 0);
#if __arm64__
proc_legacy_footprint_entitled(p, new_task, __FUNCTION__);
#endif /* __arm64__ */
/* Sever any extant thread affinity */
thread_affinity_exec(current_thread());
/* Inherit task role from old task to new task for exec */
if (!in_vfexec) {
proc_inherit_task_role(new_task, old_task);
}
thread_t main_thread = imgp->ip_new_thread;
task_set_main_thread_qos(new_task, main_thread);
#if CONFIG_ARCADE
/*
* Check to see if we need to trigger an arcade upcall AST now
* that the vnode has been reset on the task.
*/
arcade_prepare(new_task, imgp->ip_new_thread);
#endif /* CONFIG_ARCADE */
#if CONFIG_MACF
/*
* Processes with the MAP_JIT entitlement are permitted to have
* a jumbo-size map.
*/
if (mac_proc_check_map_anon(p, 0, 0, 0, MAP_JIT, NULL) == 0) {
vm_map_set_jumbo(get_task_map(new_task));
vm_map_set_jit_entitled(get_task_map(new_task));
}
#endif /* CONFIG_MACF */
if (vm_darkwake_mode == TRUE) {
/*
* This process is being launched when the system
* is in darkwake. So mark it specially. This will
* cause all its pages to be entered in the background Q.
*/
task_set_darkwake_mode(new_task, vm_darkwake_mode);
}
#if CONFIG_DTRACE
dtrace_thread_didexec(imgp->ip_new_thread);
if ((dtrace_proc_waitfor_hook = dtrace_proc_waitfor_exec_ptr) != NULL) {
(*dtrace_proc_waitfor_hook)(p);
}
#endif
#if CONFIG_AUDIT
if (!error && AUDIT_ENABLED() && p) {
/* Add the CDHash of the new process to the audit record */
uint8_t *cdhash = cs_get_cdhash(p);
if (cdhash) {
AUDIT_ARG(data, cdhash, sizeof(uint8_t), CS_CDHASH_LEN);
}
}
#endif
if (in_vfexec) {
vfork_return(p, retval, p->p_pid);
}
} else {
DTRACE_PROC1(exec__failure, int, error);
}
exit_with_error:
/*
* clear bsd_info from old task if it did exec.
*/
if (task_did_exec(old_task)) {
set_bsdtask_info(old_task, NULL);
}
/* clear bsd_info from new task and terminate it if exec failed */
if (new_task != NULL && task_is_exec_copy(new_task)) {
set_bsdtask_info(new_task, NULL);
task_terminate_internal(new_task);
}
if (imgp != NULL) {
/* Clear the initial wait on the thread transferring watchports */
if (imgp->ip_new_thread) {
task_clear_return_wait(get_threadtask(imgp->ip_new_thread), TCRW_CLEAR_INITIAL_WAIT);
}
/* Transfer the watchport boost to new task */
if (!error && !in_vfexec) {
task_transfer_turnstile_watchports(old_task,
new_task, imgp->ip_new_thread);
}
/*
* Do not terminate the current task, if proc_exec_switch_task did not
* switch the tasks, terminating the current task without the switch would
* result in loosing the SIGKILL status.
*/
if (task_did_exec(old_task)) {
/* Terminate the current task, since exec will start in new task */
task_terminate_internal(old_task);
}
/* Release the thread ref returned by fork_create_child */
if (imgp->ip_new_thread) {
/* wake up the new exec thread */
task_clear_return_wait(get_threadtask(imgp->ip_new_thread), TCRW_CLEAR_FINAL_WAIT);
thread_deallocate(imgp->ip_new_thread);
imgp->ip_new_thread = NULL;
}
}
/* Release the ref returned by fork_create_child */
if (new_task) {
task_deallocate(new_task);
new_task = NULL;
}
if (should_release_proc_ref) {
proc_rele(p);
}
if (bufp != NULL) {
FREE(bufp, M_TEMP);
}
if (inherit != NULL) {
ipc_importance_release(inherit);
}
return error;
}
其中主要的逻辑是构造image_params。其定义如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53struct image_params {
user_addr_t ip_user_fname; /* argument 文件名*/
user_addr_t ip_user_argv; /* argument 参数*/
user_addr_t ip_user_envv; /* argument 环境参数*/
int ip_seg; /* segment for arguments 参数段*/
struct vnode *ip_vp; /* file 文件*/
struct vnode_attr *ip_vattr; /* run file attributes,run文件属性*/
struct vnode_attr *ip_origvattr; /* invocation file attributes,invocation文件属性*/
cpu_type_t ip_origcputype; /* cputype of invocation file ,invocation文件的cpu类型*/
cpu_subtype_t ip_origcpusubtype; /* subtype of invocation file ,invocation文件的cpu子类型*/
char *ip_vdata; /* file data (up to one page),文件数据(最多一页)*/
int ip_flags; /* image flags,标志位*/
int ip_argc; /* argument count,参数计数*/
int ip_envc; /* environment count,环境变量计数*/
int ip_applec; /* apple vector count,apple向量计数*/
char *ip_startargv; /* argument vector beginning,参数向量开始*/
char *ip_endargv; /* end of argv/start of envv,argv结束/envv开始*/
char *ip_endenvv; /* end of envv/start of applev,envv结束/applev开始*/
char *ip_strings; /* base address for strings,字符串的基址*/
char *ip_strendp; /* current end pointer,当前end指针*/
int ip_argspace; /* remaining space of NCARGS limit (argv+envv),NCARGS限制(argv+envv)中剩下的空间*/
int ip_strspace; /* remaining total string space,总字符串空间剩下的空间*/
user_size_t ip_arch_offset; /* subfile offset in ip_vp,ip_vp中子文件的偏移*/
user_size_t ip_arch_size; /* subfile length in ip_vp,ip_vp中子文件的长度*/
char ip_interp_buffer[IMG_SHSIZE]; /* interpreter buffer space,解释器缓冲区*/
int ip_interp_sugid_fd; /* fd for sugid script,sugid脚本的fd*/
/* Next two fields are for support of architecture translation... ,下面两个字段用于架构的翻译*/
struct vfs_context *ip_vfs_context; /* VFS context vfs上下文 */
struct nameidata *ip_ndp; /* current nameidata 当前的nameidata*/
thread_t ip_new_thread; /* thread for spawn/vfork,用于vfor/或者spawn的线程*/
struct label *ip_execlabelp; /* label of the executable,可执行文件的标签*/
struct label *ip_scriptlabelp; /* label of the script,脚本标签*/
struct vnode *ip_scriptvp; /* script 脚本*/
unsigned int ip_csflags; /* code signing flags 签名标志位*/
int ip_mac_return; /* return code from mac policy checks */
void *ip_px_sa;
void *ip_px_sfa;
void *ip_px_spa;
void *ip_px_smpx; /* MAC-specific spawn attrs. */
void *ip_px_persona; /* persona args */
void *ip_px_pcred_info; /* posix cred args */
void *ip_cs_error; /* codesigning error reason */
uint64_t ip_dyld_fsid;
uint64_t ip_dyld_fsobjid;
unsigned int ip_simulator_binary; /* simulator binary flags */
};
__\mac_execve函数的主要流程如下:
- 创建相关结构体指针。
- 为imgp申请大块内存。
- 设置线程信息:(vfork则直接设置标记,否则重新创建线程)。
- 执行加载imgp。
接下来是执行激活二进制
exec_activate_image
1 | static int |
关于namei的相关内容可查看这里。
exec_activate_image函数的主要作用是进行二进制文件的查找和加载到内存中,最后由execsw数组中的函数指针来执行具体的二进制加载,其中execsw的结构如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9struct execsw {
int(*const ex_imgact)(struct image_params *);
const char *ex_name;
}const execsw[] = {
{ exec_mach_imgact, "Mach-o Binary" },
{ exec_fat_imgact, "Fat Binary" },
{ exec_shell_imgact, "Interpreter Script" },
{ NULL, NULL}
};
exec_activate_image函数的流程如下:
- 从vfs上下文环境中获得 proc_t。
- 分配内核内存用于保存用户空间的参数和镜像的第一个页面。
- 保存程序路径并修正参数。
- 使用namei() 和 NDINIT宏来获取镜像文件。
- 确保进程中没有其他线程执行exit,并标记二进制文件转换开始。
- 权限检查。
- 将第一个页面加载到内存中。
- 遍历execsw数组,执行对应的函数。
这里是MachO类型,所以执行exec_mach_imgact
exec_mach_imgact
该函数比较长,这里不在给出源码,占用篇幅。该函数主要流程如下:
- 分析macho的头文件架构(64or32)。
- 对二进制进行分析评估是否满足加载要求,其中包括cpu类型等
- 针对
__\mac_execve函数中的vfork标记来创建任务和线程(vfork不会创建任务和线程)。 - 调用
load_machfile加载二进制文件
load_machfile
load_machfile函数负责设置内存映射,并最终加载各种LC_SEGMENT命令加载的内容。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240oad_return_t
load_machfile(
struct image_params *imgp,//镜像参数
struct mach_header *header,
thread_t thread,//current_thread
vm_map_t *mapp,
load_result_t *result//加载结果
)
{
struct vnode *vp = imgp->ip_vp;
off_t file_offset = imgp->ip_arch_offset;
off_t macho_size = imgp->ip_arch_size;
off_t file_size = imgp->ip_vattr->va_data_size;
pmap_t pmap = 0; /* protected by create_map */
vm_map_t map;
load_result_t myresult;
load_return_t lret;
boolean_t enforce_hard_pagezero = TRUE;
int in_exec = (imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_EXEC);
task_t task = current_task();
int64_t aslr_page_offset = 0;
int64_t dyld_aslr_page_offset = 0;
int64_t aslr_section_size = 0;
int64_t aslr_section_offset = 0;
kern_return_t kret;
unsigned int pmap_flags = 0;
if (macho_size > file_size) {
return LOAD_BADMACHO;
}
result->is_64bit_addr = ((imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_IS_64BIT_ADDR) == IMGPF_IS_64BIT_ADDR);
result->is_64bit_data = ((imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_IS_64BIT_DATA) == IMGPF_IS_64BIT_DATA);
#if defined(HAS_APPLE_PAC)
pmap_flags |= (imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_NOJOP) ? PMAP_CREATE_DISABLE_JOP : 0;
#endif /* defined(HAS_APPLE_PAC) */
pmap_flags |= result->is_64bit_addr ? PMAP_CREATE_64BIT : 0;
task_t ledger_task;
if (imgp->ip_new_thread) {
ledger_task = get_threadtask(imgp->ip_new_thread);
} else {
ledger_task = task;
}
//创建新的pmap
pmap = pmap_create_options(get_task_ledger(ledger_task),
(vm_map_size_t) 0,
pmap_flags);
if (pmap == NULL) {
return LOAD_RESOURCE;
}
//创建新的vmmap
map = vm_map_create(pmap,
0,
vm_compute_max_offset(result->is_64bit_addr),
TRUE);
#if defined(__arm64__)
if (result->is_64bit_addr) {
/* enforce 16KB alignment of VM map entries */
vm_map_set_page_shift(map, SIXTEENK_PAGE_SHIFT);
} else {
vm_map_set_page_shift(map, page_shift_user32);
}
#elif (__ARM_ARCH_7K__ >= 2) && defined(PLATFORM_WatchOS)
/* enforce 16KB alignment for watch targets with new ABI */
vm_map_set_page_shift(map, SIXTEENK_PAGE_SHIFT);
#endif /* __arm64__ */
#ifndef CONFIG_ENFORCE_SIGNED_CODE
/* This turns off faulting for executable pages, which allows
* to circumvent Code Signing Enforcement. The per process
* flag (CS_ENFORCEMENT) is not set yet, but we can use the
* global flag.
*/
if (!cs_process_global_enforcement() && (header->flags & MH_ALLOW_STACK_EXECUTION)) {
vm_map_disable_NX(map);
// TODO: Message Trace or log that this is happening
}
#endif
/* Forcibly disallow execution from data pages on even if the arch
* normally permits it. */
if ((header->flags & MH_NO_HEAP_EXECUTION) && !(imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_ALLOW_DATA_EXEC)) {
vm_map_disallow_data_exec(map);
}
/*
* Compute a random offset for ASLR, and an independent random offset for dyld.
*/
//计算ASLR
if (!(imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_DISABLE_ASLR)) {
vm_map_get_max_aslr_slide_section(map, &aslr_section_offset, &aslr_section_size);
aslr_section_offset = (random() % aslr_section_offset) * aslr_section_size;
aslr_page_offset = random();
aslr_page_offset %= vm_map_get_max_aslr_slide_pages(map);
aslr_page_offset <<= vm_map_page_shift(map);
dyld_aslr_page_offset = random();
dyld_aslr_page_offset %= vm_map_get_max_loader_aslr_slide_pages(map);
dyld_aslr_page_offset <<= vm_map_page_shift(map);
aslr_page_offset += aslr_section_offset;
}
if (!result) {
result = &myresult;
}
*result = load_result_null;
/*
* re-set the bitness on the load result since we cleared the load result above.
*/
result->is_64bit_addr = ((imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_IS_64BIT_ADDR) == IMGPF_IS_64BIT_ADDR);
result->is_64bit_data = ((imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_IS_64BIT_DATA) == IMGPF_IS_64BIT_DATA);
//解析加载对应的macho
lret = parse_machfile(vp, map, thread, header, file_offset, macho_size,
0, aslr_page_offset, dyld_aslr_page_offset, result,
NULL, imgp);
//加载失败,返还内存
if (lret != LOAD_SUCCESS) {
vm_map_deallocate(map); /* will lose pmap reference too */
return lret;
}
#if __x86_64__
/*
* On x86, for compatibility, don't enforce the hard page-zero restriction for 32-bit binaries.
*/
if (!result->is_64bit_addr) {
enforce_hard_pagezero = FALSE;
}
/*
* For processes with IMGPF_HIGH_BITS_ASLR, add a few random high bits
* to the start address for "anywhere" memory allocations.
*/
#define VM_MAP_HIGH_START_BITS_COUNT 8
#define VM_MAP_HIGH_START_BITS_SHIFT 27
if (result->is_64bit_addr &&
(imgp->ip_flags & IMGPF_HIGH_BITS_ASLR)) {
int random_bits;
vm_map_offset_t high_start;
random_bits = random();
random_bits &= (1 << VM_MAP_HIGH_START_BITS_COUNT) - 1;
high_start = (((vm_map_offset_t)random_bits)
<< VM_MAP_HIGH_START_BITS_SHIFT);
vm_map_set_high_start(map, high_start);
}
#endif /* __x86_64__ */
/*
* Check to see if the page zero is enforced by the map->min_offset.
*/
if (enforce_hard_pagezero &&
(vm_map_has_hard_pagezero(map, 0x1000) == FALSE)) {
#if __arm64__
if (!result->is_64bit_addr && /* not 64-bit address space */
!(header->flags & MH_PIE) && /* not PIE */
(vm_map_page_shift(map) != FOURK_PAGE_SHIFT ||
PAGE_SHIFT != FOURK_PAGE_SHIFT) && /* page size != 4KB */
result->has_pagezero && /* has a "soft" page zero */
fourk_binary_compatibility_unsafe) {
/*
* For backwards compatibility of "4K" apps on
* a 16K system, do not enforce a hard page zero...
*/
} else
#endif /* __arm64__ */
{
vm_map_deallocate(map); /* will lose pmap reference too */
return LOAD_BADMACHO;
}
}
vm_commit_pagezero_status(map);
/*
* If this is an exec, then we are going to destroy the old
* task, and it's correct to halt it; if it's spawn, the
* task is not yet running, and it makes no sense.
*/
if (in_exec) {
proc_t p = vfs_context_proc(imgp->ip_vfs_context);
/*
* Mark the task as halting and start the other
* threads towards terminating themselves. Then
* make sure any threads waiting for a process
* transition get informed that we are committed to
* this transition, and then finally complete the
* task halting (wait for threads and then cleanup
* task resources).
*
* NOTE: task_start_halt() makes sure that no new
* threads are created in the task during the transition.
* We need to mark the workqueue as exiting before we
* wait for threads to terminate (at the end of which
* we no longer have a prohibition on thread creation).
*
* Finally, clean up any lingering workqueue data structures
* that may have been left behind by the workqueue threads
* as they exited (and then clean up the work queue itself).
*/
kret = task_start_halt(task);
if (kret != KERN_SUCCESS) {
vm_map_deallocate(map); /* will lose pmap reference too */
return LOAD_FAILURE;
}
proc_transcommit(p, 0);
workq_mark_exiting(p);
task_complete_halt(task);
workq_exit(p);
/*
* Roll up accounting info to new task. The roll up is done after
* task_complete_halt to make sure the thread accounting info is
* rolled up to current_task.
*/
task_rollup_accounting_info(get_threadtask(thread), task);
}
*mapp = map;
#ifdef CONFIG_32BIT_TELEMETRY
if (!result->is_64bit_data) {
/*
* This may not need to be an AST; we merely need to ensure that
* we gather telemetry at the point where all of the information
* that we want has been added to the process.
*/
task_set_32bit_log_flag(get_threadtask(thread));
act_set_astbsd(thread);
}
#endif /* CONFIG_32BIT_TELEMETRY */
return LOAD_SUCCESS;
}
该函数主要分为以下几个部分:
- 进行内存映射。
- 完善一些安全性设置,包括ASLR,禁用数据段执行。
- 调用
parse_machfile,负责实际的加载工作 - 如果加载失败则返还前面映射内存
- 否则更新新的内存对象
mappparse_machfile
1 | static |
函数较长。具体总结流程如下:
- 进行加载之前的文件,参数,架构检测。
进入switch环节:
- 只有深度为1的时候才执行
MH_EXECUTE。 - 只有深度为2的时候才执行
MH_DYLINKER。 - 其他的异常返回
LOAD_FAILURE。
- 只有深度为1的时候才执行
把所有指令都映射进内存。
- 根据
PIE和dyld设置ASLR。 - 进行3轮扫描
- 根据switch分支加载响应的动作。
LC_SEGMENT/LC_SEGMENT_64:调用具体的 load_segment()。根据段指令将段直接映射进内存。LC_UNIXTHREAD:调用load_unixthread()。LC_MAIN:调用load_main()。LC_LOAD_DYLINKER:如果在第3轮调且深度为1,则将命令保存到dlp变量中。LC_UUID:调用load_uuid()。将UUID复制到结果中。LC_CODE_SIGNATURE:调用load_code_signature(),只有第一趟扫描中。但是暂不验证。- 还有一些其他的命令将会被忽略,由后面的
dylinker来完成。
- 这3趟循环结束之后,
dlp变量中有一个保存的动态链接器命令。 将动态链接器加载到新的映射中,可能要根据ASLR进行调整,load_dylinker函数会继续递归调用parse_machfile
至此。machO 已经被映射到内存中。接下来会在DYLD的流程中进行动态库的插入,加载,链接,及rebase。然后执行相关的初始化函数。最终返回main。
总结
app启动前发生的事情。
- 由用户态触发进程创建。
- 通过系统调用执行内核创建进程。
- 读取镜像文件。加载header到内存
- 遍历excsw,执行对应的二进制格式加载逻辑
- 加载,解析对应的macho命令
- 保存dyld命令。
- 内核态完成。交由dyld进行动态库处理